During manufacturing textile, stable product quality and production efficiency never occurs occasionally. Every evenly dyed and batch-consistent fabric is inseparable from the scientifically designed textile process and a well-matched textile auxiliary system.
For overseas dyeing mills, textile fabric manufacturers and textile chemical distributors, a comprehensive understanding of the textile technological process not only helps solve practical problems in production, but also helps to achieve a balance among cost control, process stability and final fabric performance when selecting auxiliaries.
This article will systematically disassemble the textile dyeing and finishing process, which starts from each key procedure and analyzes the role of bahan pembantu tekstil in improving production stability and the quality of finished products.

Pretreatment Process: The Foundation of Successful Dyeing
Before dyeing process, the grey fabric needs pretreatment to remove various kinds of impurities that may affect dyeing and finishing effect.
Main Purpose of Pretreatment
- Removes natural impurities (such as was, pectin and grease)
- Removes the residual auxiliary during spinning and weaving processes
- Improves moisture absorption and wetting performance of fabric
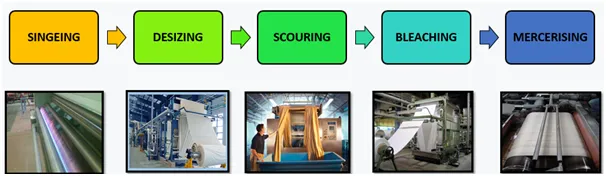
Common Pretreatment Process
- Singeing
- Desizing (mainly for woven fabrics)
- Boiling and scouring
- Pemutihan (depends on the product requirements)
- Mercerizing
Functions of Alat Bantu Tekstil
- Agen pembasah: Improves the wetting ability of working solution into fabric
- Scouring agent, emulsifying agent: Effectively removes grease and wax
- Sequestering agent: Controls the metal ions in water to stabilize the process
- Bleaching stabilizer: Protects the hydrogen peroxide system to prevent damaging fibers
Whether the pretreatment effect is even directly determines the consistency and reproducibility of the subsequent dyeing.
Dyeing Process: The Crucial Stage to Determine Color and Evenness
Dyeing is the most crucial link in the entire textile process. Dyeing depth, evenness and color fastness are formed in this stage. Different fibers are adopted different dyeing systems.
Common Fibers and Dye System
- Poliester → Disperse dyes
- Kapas → Reactive dyes or vat dyes
- Nilon → Acid dyes
- Blended fabric → Step by step or one bath with multiple dyeing
Commonly Seen Problems during Dyeing Process
- Uneven dyeing
- Color differences between batches
- Insufficient wetting of dyes in tight fabric
- Unstable dyeing curve
Commonly Used Alat Bantu Pencelupan
- Dispersing agent: Keeps dyes dispersing stably
- Leveling agent: Controls dye uptake of dyes
- Polyester dyeing carrier: Improves dyeing effect at low temperature or in special condition
- pH buffering agent and dyeing bath stabilizer
Choosing auxiliaries reasonably according to the type of fibers and dyeing condition is helpful to reduce rework, decrease color modifying rate and improve first-passyield.
Aftertreatment Process: Improves Color Fastness and Color Stability
After dyeing, fabrics often need to have aftertreatment to remove the unfixed dyes, so as to improve color fastness.
Main Aftertreatment Steps
- Reduction clearing (mainly for dyeing of polyester)
- Soaping, water washing
- Neutralizing
Aftertreatment Effect
- Improves color fastness to washing and rubbing
- Luster can be clearer and cleaner
- Reduces staining in subsequent garment washing
The reasonable use of high-efficiency soaping agent and low-foaming washing auxiliary can ensure quality as well as reduce water consumption and energy consumption at the same time.
Finishing Process: Imparts Fabrics the Final Performance
Finishing is the stage to adjust he functionality and handle of fabric according to its final use.
Common Targets of Finishing
- Soft handle
- Smoothness and anti-pilling performance
- Water repellency, moisture absorption and quick-drying performance
- Anti-creasing performance and dimensional stability
Common Agen Finishing
- Pelembut silikon
- Hydrophilic finishing agent
- Anti-static finishing agent
- Resin finishing agents
The compatibility of finishing agent and previous dyeing process is especially important. Poor compatibility will cause color changing, uneven handle or performance decreasing after water washing.

Process Optimization: The Importance of Choosing Auxiliaries
In many dyeing mills, quality problems are often remedied by increasing the temperature or extending the time. But in the long term, to optimize the process by choosing reasonable auxiliaries is a more stable and economical solution.
High-quality bahan pembantu tekstil can:
- Adapt to different water quality conditions, which makes production stable
- Decrease risks of reworking and re-dyeing
- Improve the overall production efficiency
- Ensure the consistency among different equipment and batches
For dyeing mills and textile chemical distributors, choosing suppliers who really understand the production process is far more valuable than using general-purpose products.

Support the Optimization of Full Process of Textile Technology with a Complete Product System
In the actual production, a single auxiliary often fails to solve complicated process problems. Really stable and replicable dyeing and finishing effect relies on a textile auxiliaries system covering the entire process and a deep understanding on the process details.
BLUELAKECHEM is a professional enterprise focusing on researching, developing and manufacturing textile auxiliaries. Our product line is systematically laid out around the core process of textile processing. We can provide more well-matched solutions for customers with different fiber types and process conditions.

