Before dyeing and finishing, pretreatment is a key link to determine the quality of final fabric. Whether it is natural fibers such as cotton and flax, etc. or synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, etc., the quality of the pretreatment directly affects the evenness of dyeing, dyeing efficiency, color fastness and the effect of subsequent functional finishing. This article will systematically disassemble the objective of pretreatment, common processes, typical process parameters, commonly used auxiliaries and practical suggestions to help factory engineers, technical purchasers and chemical distributors to make wiser decisions on process and product.

The Overall Purpose and Quality Index of Pretreatment
Core Purpose
1. Removes processing residues from the fabric (Sizing, grease, lubricant, ink smudge and residue of bahan bantu tekstil, etc.)
2. Improves moisture absorption and wetting performance of fabrics to make sure that dyes will disperse evenly among the fibers.
3. Removes pigment or natural impurities (Such as pectin, wax and natural pigments in cotton) to facilitate subsequent bleaching or dyeing.
4. Controls the water quality and metal ions to prevent dyeing defects caused by metal ions.

Common Quality Judgment Items
- Time of absorbing water / wetting performance (The shorter, the better).
- Residual greasy dirt on the surface (White light or microscopic examination).
- Whiteness value after bleaching (For grey cloth that needs bleaching).
- Visual color difference and evenness of dyeing (As an indirect indicator for subsequent processes).
Common Pretreatment Processes and Their Functions
1. Desizing
Applicable objects: Fabrics containing starch/synthetic sizing agents, such as woven grey fabric and warp knitted fabric, etc.
Purpose: Removes sizing agents and restores the moisture absorption of fibers and the openness of feathers.
Common methods:
- Enzymic method: α-amylase decomposes starch slurry under neutral or weakly alkaline conditions, which is mild and environmentally-friendly.
- Alkali method or acid method: It is aiming at the formulas of synthetic sizing agent or compound sizing agent, depending on the component of sizing agents.
Typical parameters for reference: Enzymic method: 50~60℃, pH: 6~8, Time: 30~60 minutes (depending on the content of sizing agent)
Commonly used auxiliaries: Zymin, corrosion inhibitor,wetting agent, low-foaming emulsifying agent
2. Boiling and Scouring / Alkali Cleaning
Applicable objects: Removes wax, pectin and grease on natural fibers (especially cotton).
Purpose: Saponifies and emulsifies the impurities on the surface of the fibers, then removes them, so as to improve the moisture absorption.
Method and parameters: Alkali scouring (generally use NaOH or mixed alkalis). Temperature can be up to 95~100℃. Time depends on the fabric (20~60 minutes).
Alternative solution: Biological enzyme scouring can achieve removing grease under mild conditions. It has low energy consumption, minimal fiber damage, which is more environmentally-friendly.
Commonly used auxiliaries: Strong agen penyahgris, wetting agent, emulsifying agent, agen penyitaan, corrosion inhibitor, hydrogen peroxide stabilizer (depends on whether there is bleaching or not in the following process).
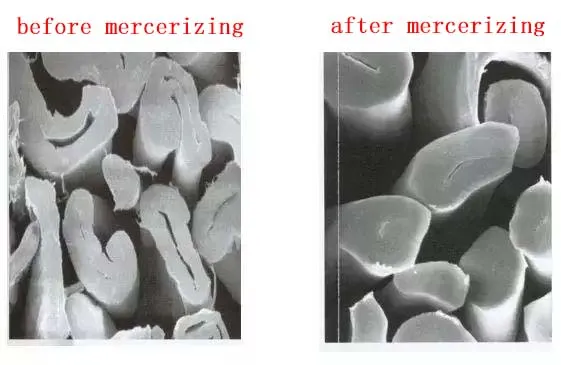
3. Bleaching
Applicable objects: The grey fabric (especially cotton fabric) that needs to achieve higher whiteness or remove natural pigment.
Common system: Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) bleaching is the most common. And it is in alkali or neutral condition and added stabilizer.
Typical parameters for reference: Temperature: 80~95℃, pH: 9~10, Time is depending on the depth of bleaching.
Important point: Hydrogen peroxide needs to be used together with stabilizer and sustained-release system to protect fibers and prevent yellowing. The neutralizing and thorough cleaning after bleaching is very essential.
Commonly used auxiliaries: Hydrogen peroxide stabilizer, complexing agent, peroxidase inhibitor, neutralizing agent and wetting agent.

4. Neutralizing and Soaping
Purpose: Neutralizes the residual alkali and removes residual chemicals and loose dye molecules, so as to create a clean and stable base fabric state for dyeing.
Steps: Adjusts the pH to neutral or slightly acid with an acid neutralizing agent after bleaching or alkali boiling, then has soaping/water washing to thoroughly remove soluble residue.
Commonly used auxiliaries: Low-foaming soaping agent, neutralizing agent and agen penyahgris.
5. Water washing and dewatering
Purpose: Thoroughly removes the by-products of the reaction to avoid affecting dyeing or causing color differences.
Key points of practice: Pays attention to water quality, the number and flow rate of washing. Uses efficient dewatering or pressing processes, which can reduce the water consumption in subsequent treatment.
Mengenai BLUELAKECHEM
BLUELAKECHEM has been focusing on researching, developing and manufacturing textile auxiliaries. We provide long-term service to dyeing mills, weaving factories and chemical distributors. We provide a complete product range covering the entire pretreatment process, including but not limited to wetting agent, desizing zymin, degreasing agent, emulsifying, agen penyitaan, hydrogen peroxide stabilizer and low-foaming soaping agent. At the same time, we provide technical support to customers from small sample tests to on-site process formula adjustments, helping factories to achieve the goals of process stability, energy consumption and wastewater optimization.
In addition, BLUELAKECHEM has the entire product line covering dyeing process, functional finishing, silicone oil and soft finishing series. We can provide customers with an integrated solution covering pretreatment, dyeing and functional finishing. If you need further technical data, sample testing or process consultant, we can provide customized suggestions and sample test support according to your fabric types and equipment condition.


